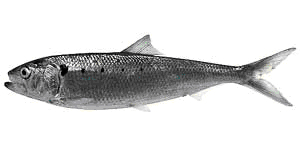
GARDA LAKE FISH
AGONE
Common name: sardina, sardèlla, sardéna.
Description: maximum size around 35 to 40 cm, usually about 25 cm with 50 gr. weight, maximum life of 7-8 years. Sides of silver, bluish-green back, white belly, black spots from the eye to the middle of the side, under the abdomen has a ventral fairing.
Feeding: feeds on plankton, small crustaceans, insect larvae, insects and small fish.
Habits: Of marine origins and migration, become stationary in the lake basins, live in herds of thousands of fish in winter is between 50 and 100 m, with some climbs on the surface, in the spring approaches the shore and towards the end of May and June look places of spawning in deep water close to shore. The eggs hatch in 2-8 days
Flesh: slightly fatty meat and tasty, best in the winter months when it is more stout.
Conservation: dried, salted
Cooking: grilled, in saor,
Fishing: from a boat or from shore with ametiere five hooks with artificial lures
History: Given the number and the life of the group, was for centuries, with the bleak, a staple food and the income of fishermen del Garda
ALBORELLA
Common name: àola, àgola, àvola, pessàta
Description: green back, silvery sides and a white belly, small scales with mother of pearl reflections, mouth turned slightly upward, its size does not exceed 20 cm.
Feeding: feeds on plankton, larvae, insects and plant debris.
Habits: lives in numerous flocks near the surface of stagnant water that is current, you play by the end of May to August, when it goes into care at night along the beach laying eggs on plants and gravel funds. Its eggs hatch after four to five days at a temperature of 20 °
Flesh: tasty meat both before and during the spawning season, like during the summer months for the recruitment of plants.
Conservation: dried, pickled, salted
Cooking: aole fried, in “sisam”,
Fishing: with nets,
History: As the arena was the basis of income and food for the people of the lake for centuries, now the number is greatly reduced and its fishery has been regulated.
Curiosity: its scales is extracted a substance (essence of ‘East) used in the manufacture of artificial pearls.
Anguilla
Common name: anguìla, anguèla, bisàto, capitone
Description:body elongated snake-circular cross-section, the dorsal fin is united with that of the tail (caudal) and the anal, missing ventral fins, the head is slightly elongated with prominent jaw and small teeth, scales small, is covered with a lot of mucus that makes it very slippery, very dark back and light belly, whitish yellow, when it reaches adulthood becomes darker on the back. Usually measures about 50 cm, but also reaches 140 cm and weighs between 200 grams to 4 kg. Females are larger than males.
Habitat: prefers the banks of the lake and live constantly in the background, preferably muddy, also lives in rivers, canals, ditches, ponds and adapts to any place of fresh water.
Feeding: feeds on insects, invertebrates of the seabed, crustaceans, worms, insect larvae, molluscs, small fish from the lake and fish eggs; stops feeding during playback
Habits: voracious predator that hunts at night
Flesh: depending on age can be quite greasy, the meat is white, tender and tasty.
Conservation: smoking
Cooking: grilled, marinated, tomato, fried
Fishing: bottom fishing at night
Bottatrice
Common name: bòsa
Description: Its shape resembles that of a tadpole, is a fish from the cylindrical body frontally which then goes flattening laterally towards the tail; the head is flattened and large, as well as the mouth, that is in the lower position and provided with small curved teeth, the jaw is provided with a barb that uses to hunt. The eyes are small, the small scales and covered with mucus, and the anal fins of the back are long to include almost the tail, the pectoral and ventral fins are modest in size and located just behind the head. Its color is dark brown, mottled light brown or yellowish. The dimensions are usually hovering about 35 cm, but can reach up to 60 cm long and 4 pounds.
Habitat: fish is a deep, usually lives between 30 and 200 m, prefers cool, clear water, without current.
Feeding: carnivorous, feeding on fish, fish eggs, crustaceans, insects, but also waste the meat for slaughter
Habits: voracious predator at night is disturbed by the light, spends the day under rocks and deep dusk approaches the shore, where the water is lower and it hunts for fish, fish eggs, worms, his technique is to hide among the vegetation and use his barb to lure into a trap prey.
Reproduction: playing in the winter months from December to peak at the end of March, during which time you closer to the shore during daylight hours to spawn on gravel, in very large numbers, but with a low survival as prey other fish, especially eels, the eggs hatch in 5-7 weeks.
Flesh: white, without spines, excellent; but the rejection rate is high, about 50%.
Conservation:
Cooking:fried if small, in fillets
Fishing: with hook
Carpa
Common name: bùlbar, raina, bùlbero, bulber
Description: the body is quite stocky, top with the back arched and the abdomen erect, the head is medium in size from the line quite sharp, the mouth is protractile and is directed towards the bottom with an opening round flanked by four barbels, two shorter . The scales are very large in the variety “sevatica” considerably reduced or completely absent in the variety “mirrors” and “leather”. The color is dark brown on the back and on the sides and abdomen golden yellow, pink fins with yellow hues. Its dimensions are among the largest of the lake generally reaches 40-50 cm above the meter also measures with 30 pounds of weight.
Habitat: lives on the bottom, where there is a lot of vegetation and mud
Feeding: invertebrates, worms, aquatic plants, insects, small crustaceans, omnivorous.
Habits: mainly at night, in the cold months from the coast looking deeper waters and warmer where you dive into the mud slowing its vital functions and suspending power. As an adult becomes solitary, often remains on the seabed, through the vegetation in search of food.
Reproduction: takes place in the months of May and July, during the morning hours with average temperatures of 20 °, gathering in small groups near the shore, in waters with vegetation, on which spawn.
Flesh:. Fat, tasty intense flavor
Conservation:
Cooking: fried, in sauce
Fishing: with the barrel, bottom technique
Carpione
Common name: carpiù, carpioo
Description: similar to trout, has a slender build, with a small head and stocky, the mouth is wide enough, equipped with small sharp teeth, the scales are medium in size, the color is dark gray metallic tints on the back, silvery on the sides and white on the belly. In the upper part of the body has small dark spots irregular. The colors of the male during the spawning take darker shades. Its dimensions are on average of about 30 cm and rarely exceed 40 cm and the kilogram of weight.
Habitat: exclusive del Garda, lives in the middle to bottom of the lake as rich in nutrients; prefers deep waters and clean, generally between 100 and 200 meters.
Feeding: plancton, invertebrates
Habits: almost always remains in the central southern part of the lake, in the deep waters, rarely moves on the surface or in shallower waters.
Reproduction: there appear to be two distinct periods of play, a winter between December and January and a summer between July and August, with two different spawning, one in the upper part of the lake during the winter and one in the center south of the lake during the summer. In winter the carp are grouped to move north, clear waters and oxygenated, between 50 and 300 meters, with gravelly or rocky bottoms, here the female gets in the backdrop of the nests in which to lay their eggs after being fertilized covers and remain there for 5 to 10 weeks depending on the water temperature; at birth the fry remain a certain period in the nests and then exit and start to feed. The fact that there are two periods of care implies that there are two groups of fish that mature at different times, but this does not affect the reproductive cycle.
Flesh: compact, with few bones, white or pink depending on the feed, delicate
Conservation: in carpione
Cooking: grilled, in carpione
Fishing: nets and trolling
History:the carp was caught in large quantities until a few years ago, then the Excessive catches of this species has led to the near extinction, now coming to a critical point.
Cavedano
Common name: cavasì, cavassìno
Description: its body is slim, sturdy, round, big mouth, its scales are large and round with the edge of gray-black on the back has a greenish brown color while the sides are silvery gray and the abdomen is white with shades yellowish. Its size usually are between 30 – 40 cm at an age of 8-9 years, but can be up to about 60 cm with a weight of 4 kg.
Habitat: clear water currents also
Feeding: practically omnivorous, including small fish from the lake.
Habits: as a young man living in small herds, as an adult became more solitary.
Flesh:. White meat and very tasty, but full of bones thin
Conservation:
Cooking: meatballs, fried,
Fishing: nets, trolling, reed
Coregone lavarello
Common name: coregone, lavarello, lavarèl, coregu
Description:is elongated, silvery-white scales on the sides with large and circular, the abdomen is white, small mouth and no teeth on the back has colors ranging from olive green to gray. Generally has a length of 40 cms, but very rarely reaches up to 80 cm with a weight of four pounds.
Habitat: lives far from the coast, in deep water and fresh but that does not go to a few tens of meters
Feeding: feeds on crustaceans, plankton, larvae.
Habits: its breeding season is between December and January, during this period
Flesh:. Whites, delicate, non-greasy, very good, with a few bones, and the period in which most fat is between July and August, while in the period before and after playing the meat is stringy.
Conservation: eaten fresh, frost
Cooking: grilled, oven
Fishing: with a rod from shore (throwing away) or from a boat, fishing is prohibited in July
History: is a species added by man in 1918
Luccio
Common name: lùs, lùsso
Description: fish from the cylindrical body, slightly flattened on the sides, has camouflage colors that change depending on the environment, the back is greenish brown with darker spots, while the sides vary from green to yellow and silver motifs, and the head is large and big mouth to “duckbill” equipped with robust and protruding jaw, the teeth are strong and sharp. The caudal fin is back at the same level as the anal, to give more snap to fish during the hunt. As a young man, around the age of 3, measuring about 35 cm, as an adult, 12 years or 90 cm and weighs 6.7 pounds, and sometimes reaches more than 30 years with a length of 150 cm and a weight of about 30 pounds .
Habitat: shores of lakes and rivers, but with little current environments with a lot of vegetation water.
Feeding: small freshwater fish, frogs, small animals.
Habits: Solitaire is a clever and strong predator, helped by its coloration is hidden in the vegetation to take the prey, and also missed out by ‘water, very territorial.
Reproduction: in the months between February and May, in shallow water, shaded and grassy or muddy bottom with vegetation.
Flesh:. White, compact, tasty but a little full of bones
Conservation: consumato fresco, gelo
Cooking: boiled
Fishing: spinning from the shore or from a boat (lure), at the bottom, with float.
Persico reale
Common name: péss pèrsech, zebra
Description: the body is nearly oval, flattened on the sides ends with a fairly narrow tail, the head is large with a big mouth and the back is arched brown color, the sides vary between yellow and gray with some zebra, the abdomen is white and fins are reddish-orange, the dorsal is thorny. Can reach 35 cm and a weight of two pounds, usually measuring about twenty inches and weighs about 200g.
Habitat: lives along the shores of the lake, hidden among rocks and vegetation.
Feeding: young feed on worms and larvae, as an adult is voracious and eat even small fish.
Habits: lives in rocky bottoms, prefer open environments, where you can hide to attack their prey, but at the same shelter from predators.
Reproduction: playing in the months of April and May, to lay their eggs but prefers shallow water with vegetation and current; eggs hatch after two to three weeks.
Flesh:. Slightly pink, firm, tasty, with many bones.
Cooking: filleted, fried and fried
Fishing: barrel, with spoons or floating
Persico sole
Common name: pesce sole, péss pèrsech
Description: side has a rounded shape is flattened on the sides, the head is small with large eyes and mouth pointing upwards and the dorsal fin is large and round, at the beginning is supported by spines at the end of soft rays. Its color is green bronze with silver and blue streaks on the head and on the lower flanks, abdomen has yellow tints, and has dark spots on its back, a characteristic that has the stain on the operculum, bright orange in red and black males and females. Its size can reach up to eight inches.
Habitat: along the coast, in waters with vegetation and stony
Feeding: larvae, earthworms,
Habits: voracious,
Reproduction:
Flesh:. compact, tasty, with lots of bones
Conservation: eaten fresh, frost
Cooking: fillets, fried
Fishing: voracious, with the barrel
Tinca
Common name: tenchèll, ténca, tencoo
Description: form is robust, massive, with large tail, the head is elongated with a small mouth and fitted with two short sides bardiglio for hunting at night, the color ranges from brownish green on the back, green, yellow on the sides, yellow on white ‘abdomen, has bronze reflections. The scales are small in size and covered with mucus. Its growth is slow, generally measuring twenty to thirty cm, rarely makes it to 50 cm with a weight of about 4.3 pounds.
Habitat: prefers still water or nearly so, or muddy bottoms with lots of greenery.
Feeding: invertebrates, worms, molluscs, small crustaceans, larvae, plant debris.
Habits: moves mostly at night, lives on the bottom, among the vegetation. In the winter months slows down its vital functions entering into a kind of lethargy and “sinks” in the mud
Reproduction:between May and June went along the southern shores of Lake Garda for reproduction, which occurs with the deposition of numerous eggs of aquatic plants in shallow waters and rich vegetation, the operation is repeated several times during the two months. The eggs hatch in up to six days.
Flesh:. Enough fat, tender and tasty, not very popular, the taste of mud that can sometimes be derived from algae that they eat, but this can be avoided by leaving it to clean under running water and clean living.
Conservation:
Cooking: sauce
Fishing: thoroughly with the worm
Trota
Common name: trùta
Description: in the Garda are three varieties of this fish, one of which is native to the lake (the lake), while two were released by man for restocking (the brown trout and rainbow trout), the first is the only one that reproduces . The shape is elongated, flattened laterally, with relatively small head with a particle jaw that ends with a slightly hooked, the color on the back is dark (green-brown or green-blue) on the sides and belly are silvery hues has grayish white, the whole body is dotted with small irregular black spots on the fins also of the back, hips has a pink line. Its size usually reach 35 cm, but can reach 60 cm and 6 pounds of weight; iin captivity reaches larger.
Habitat: running water, cool, well-oxygenated, usually far from the shore, with gravelly bottoms.
Feeding: young feed on insect larvae and crustaceans, as an adult almost exclusively on small fish from the lake.
Habits: as the trout prefer cool water, depending on the season moves in depth during the warm months and during the cold surface. As a young man living in groups while leading an adult life more isolated.
Reproduction: during the months of November and December lays its eggs in the gravel bottom, low and cool, clear waters, the female gets nests in the gravel in tail flick where lays many eggs, which will hatch after about six weeks at a temperature of 10 °. Trout is one of the most popular fish used for fish in the tank.